Asymptomatic or symptomless diseases are those diseases which damage our body slowly or rapidly without our knowledge. These benign diseases cause serious damage or even death without showing any visible signs of pain, agony and discomfort until it’s too late. Prevention, routine check ups in case of a family history and proper examination of ones physical and internal health by ones own self are the only ways to avoid the diseases and treat them in early stages.
10. Coeliac/Celiac Disease
Coeliac Disease
Coeliac or Celiac disease is a problem with digesting gluten where gluten is a protein in foods like bread, crackers, and pasta etc. Symptoms might show, like unexplained weight loss despite having a normal appetite, fatigue, weakness and bloating. Some other symptoms might also surface which we may not be linking to the disease like infertility and miscarriage. Symptoms of the disease are not serious and can also be linked with a variety of other diseases, which can delay the initial diagnosis. It is also possible to have coeliac disease without any symptoms.
9. Chlamydia
Chlamydia Diagram
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection, easily spread out because it often causes no symptoms. About 75% of infections in women and 50% in men are without symptoms. Symptoms in women include: Abnormal vaginal discharge that may have an odor, bleeding between periods, painful periods, abdominal pain with fever, pain when having sex, itching or burning in or around the vagina and pain when urinating while in men the symptoms are: Small amounts of clear or cloudy discharge from the tip of the penis, painful urination, burning and itching around the opening of the penis and pain and swelling around the testicles. For diagnosis, a sample is taken from the urethra in men or from the cervix in women using a swab. The swab is then lab tested. Other tests include a urine check for the presence of the bacteria.
8. Gonorrhea
Gonnorhea Diagram
Gonorrhea is a contagious disease transmitted most often through sexual contact with an infected person. The disease is also known ad Clap or Drip. The disease is common both in men and women. It is caused by a bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, that can grow and multiply easily in mucus membranes of the body. It requires warm and humid environment to grow. The cervix (opening to the womb), uterus (womb), and fallopian tubes (egg canals) in women, and in the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body) in women and men are the best places for the bacteria growth. The bacteria can also grow in the mouth, throat, and anus. Sometimes the symptoms are so mild that they remain unnoticed. Some symptoms which might appear include: Greenish yellow or whitish discharge from the vagina, lower abdominal or pelvic pain, burning when urinating, conjunctivitis (red, itchy eyes), bleeding between periods, spotting after intercourse, burning in the throat (due to oral sex) and Painful or swollen testicles.
7. Glaucoma
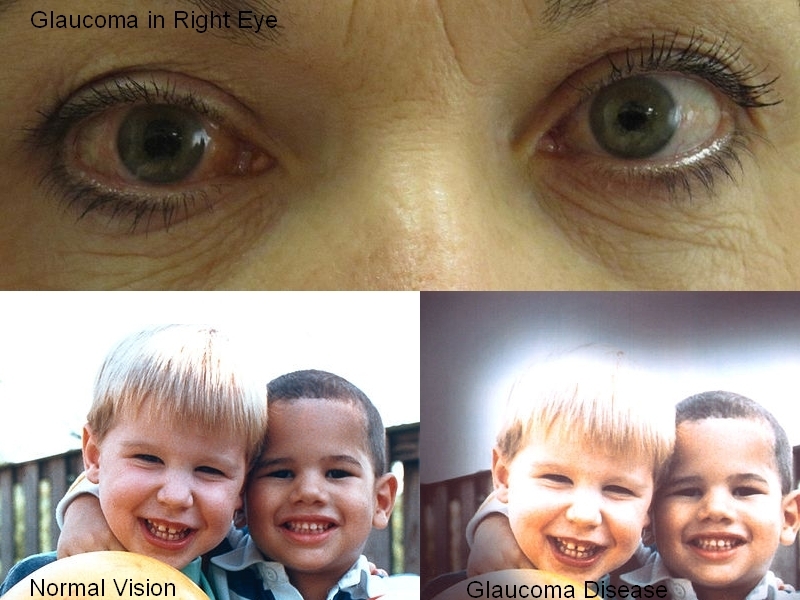
Glaucoma Disease
Optic nerve damage is known as Glaucoma. This damage ultimately leads to loss of vision (Blindness). This can happen when extra fluid builds up in the eye, such as when the eye makes too much fluid or does not drain well. Any eye injury or surgery lapse may also cause glaucoma.Types of glaucoma are: Open Angle Glaucoma, Close Angle Glaucoma and Congenital Glaucoma. Risk for the disease starts after reaching 40 years of age. An optician cannot diagnose the disease and only an ophthalmologist or an optometrist can diagnose and treat glaucoma.
6. Liposarcoma
Liposarcoma
Liposarcoma is a malignant tumor that arises in fat cells in deep soft tissue, such as that inside the thigh or in the retroperitoneum. Patients usually don’t feel any symptoms until the tumor grows to a deep seated mass in their soft tissue. Symptoms of pain or functional disturbances occur once the tumor grows big enough. Retroperitoneal tumors might show signs of weight loss and emaciation and abdominal pain. Large tumors also compress the kidney or ureter leading to organ failure. The diagnosis is established by histologic examination of the tissue, i.e. biopsy.
5. Diabetic Retinopathy
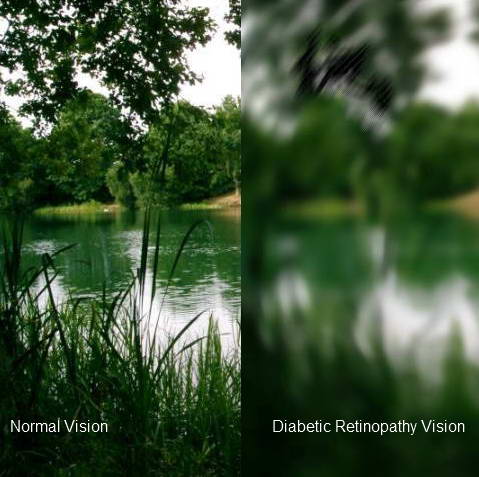

Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a disease of the eye in which damage to the retina is caused due to complications in diabetes mellitus. Retina is the part of eye that “takes pictures” and sends the images to brain. Diabetic Retinopathy eventually leads to blindness. The problem occurs if the blood sugar levels are not maintained within safe limits. New blood vessels start developing inside the eye which are weak and may burst anytime. This blood comes in the eye and affects the vision. The bleeding can also cause scar tissue to form, which can pull on the retina and cause the retina to move away from the wall of the eye. This is called retina detachment. Unfortunately the disease shows no symptoms until the vision has been affected. A regular eye examination by an eye specialist is the only way to detect and treat diabetic retinopathy in time.
4. Carotid Artery Dissection
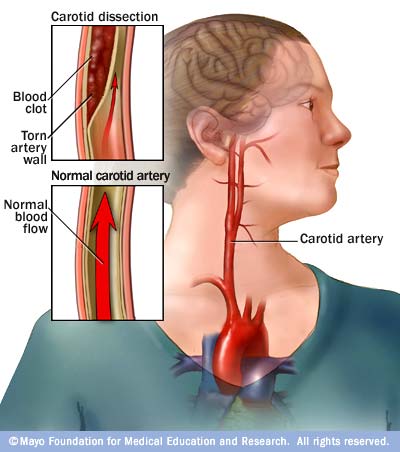
Carotid Artery Dissection
The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels that run through the neck, taking blood to the brain. This is where thinking, speech, personality, and sensory and motor functions reside. They can become narrowed from plaque buildup, hence making strokes more likely. Carotid artery dissection is a separation of the layers of the artery wall supplying oxygen-bearing blood to the head and brain, and is the most common cause of stroke in young adults. Spontaneous Carotid Dissection can occur, most frequently in the fifth decade of life. Some dissections are asymptomatic or cause only minor transient symptoms and remain undiagnosed.
3. Chronic Myelogenous (or Myeloid) Leukemia
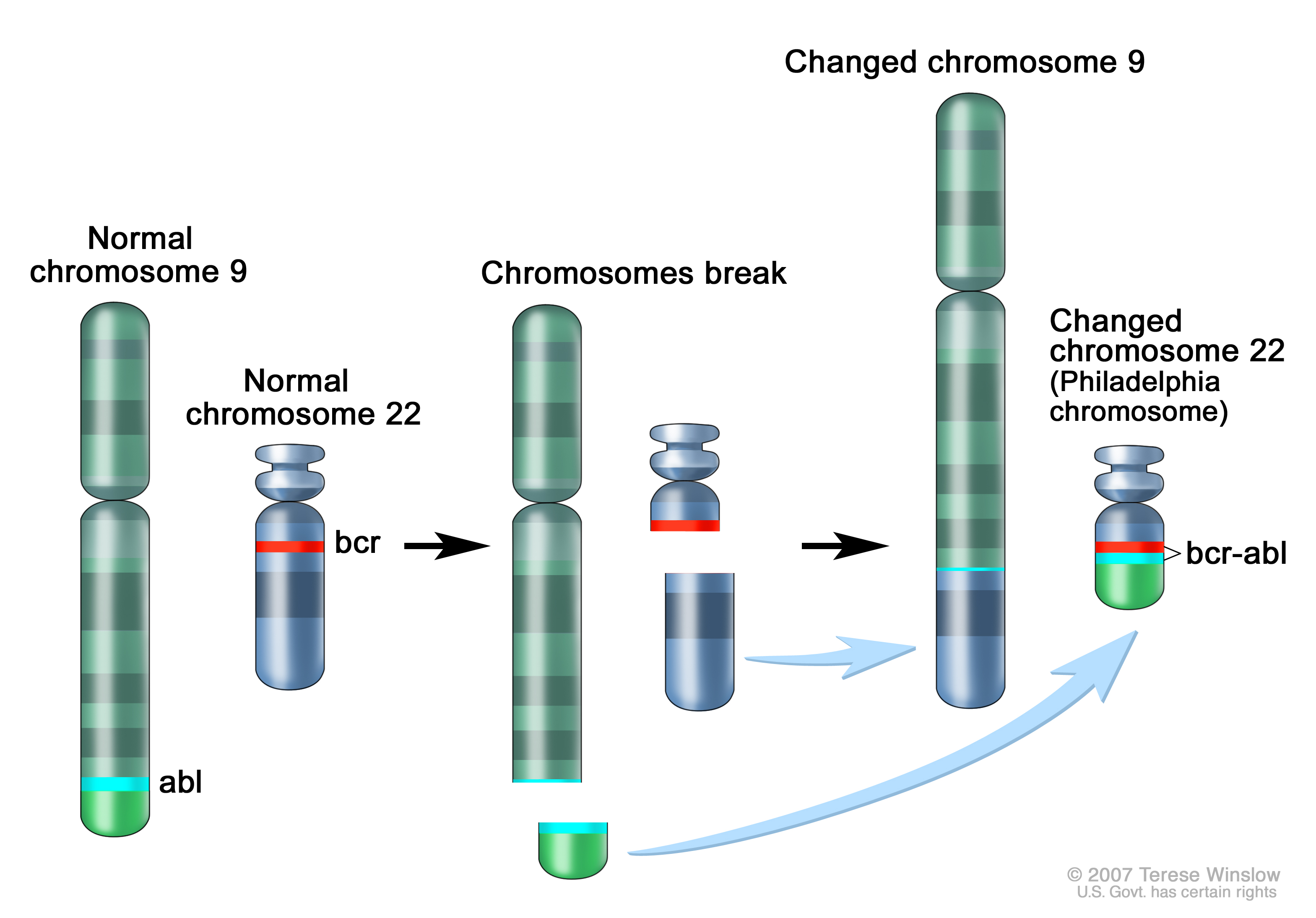
Philadelphia chromosome in Chronic Myelogenous (or Myeloid) Leukemia
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) is a type of cancer and a blood disorder in which the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells. The disease usually occurs during or after middle age, and rarely occurs in children. The white blood cells are unhealthy known as leukemic cells. CML may or not show any symptoms. The possible symptoms are fatigue, weight loss for no known reason, night sweats,f ever and pain or a feeling of fullness below the ribs on the left side. CML causes “Philadelphia Chromosome”, a disorder in which part of the DNA from one chromosome moves to another chromosome. The cancer has 3 stages, namely: Chronic Phase, Accelerated Phase and Blastic Phase. Treatments include: Surgery, Chemotherapy, Donor Lymphocyte Infusion (DLI), High-Dose Chemotherapy with Stem Cell Transplant, Biologic Therapy and Targeted Therapy.
2. Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a very dangerous asymptomatic disease that occurs when abnormal cells on the cervix grow out of control where cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. The cancer remains benign and unnoticed till it’s very advanced stages but fortunately cervical cancer can often be cured when found early. Regular Pap tests cause early detection and treatment of the deadly disease. The cancer is caused by a virus called human papillomavirus, or HPV. HPV is transmitted by having sexual contact with a partner who has it. Some symptoms include: Bleeding from the vagina that is not normal, or a change in your menstrual cycle that you can’t explain, bleeding when something comes in contact with your cervix, such as during sex or when you put in a diaphragm, pain during sex and vaginal discharge that is tinged with blood.
1. AIDS
AIDS Virus
AIDS is caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus. The virus weakens a person’s ability to fight infections and cancer. HIV transmission is caused due to unprotected sex or with needle sharing. A person may have HIV symptoms or AIDS symptoms without knowing it until they get HIV testing.